Page path:
- Press Office
- Transfer & School
- Svenja forscht
- Empty Page
Empty Page
Gesamte Seitenbreite
2-2
2-2
Gesamte Seitenbreite
1-3
2-2
Gesamte Seitenbreite
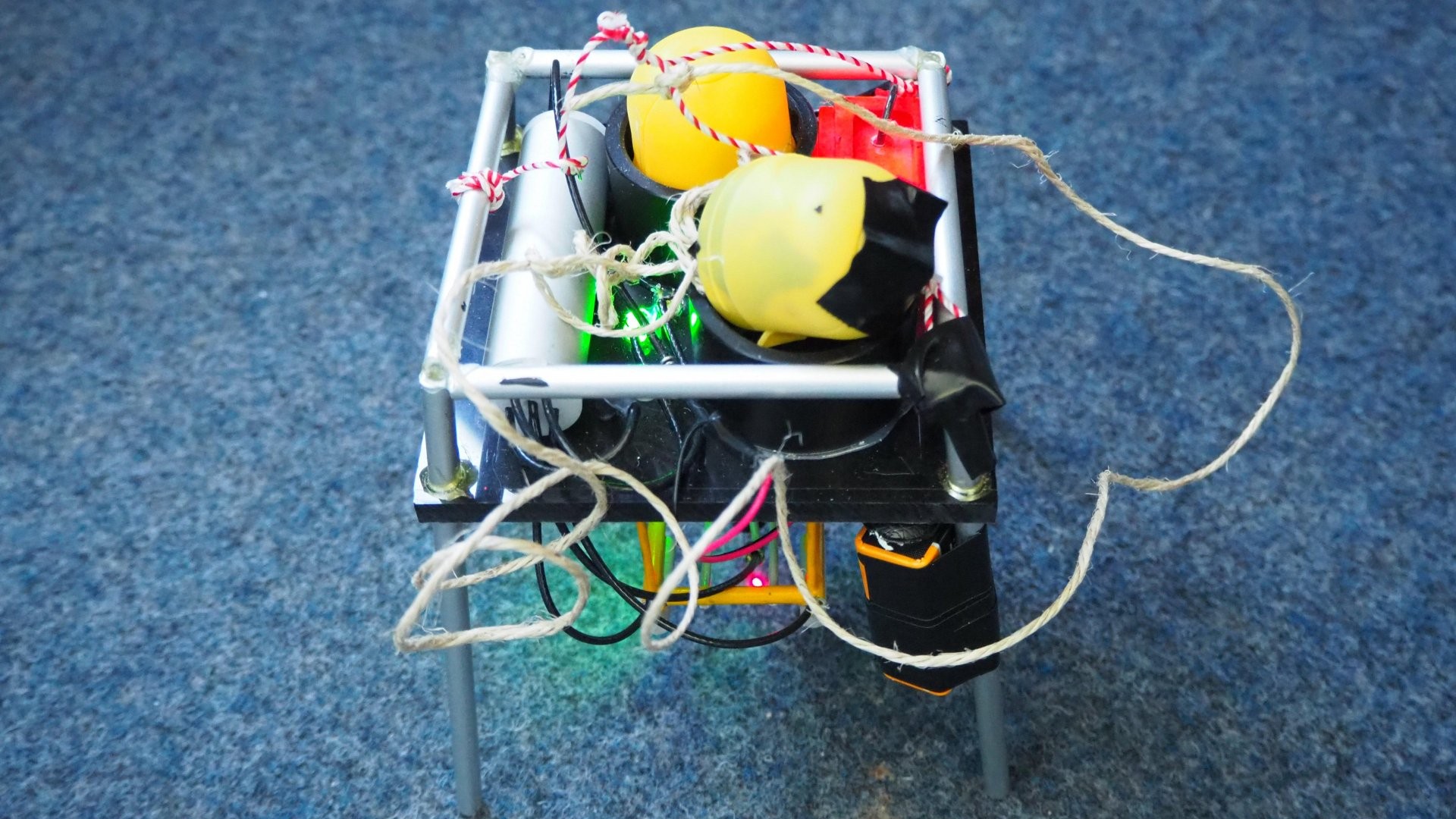
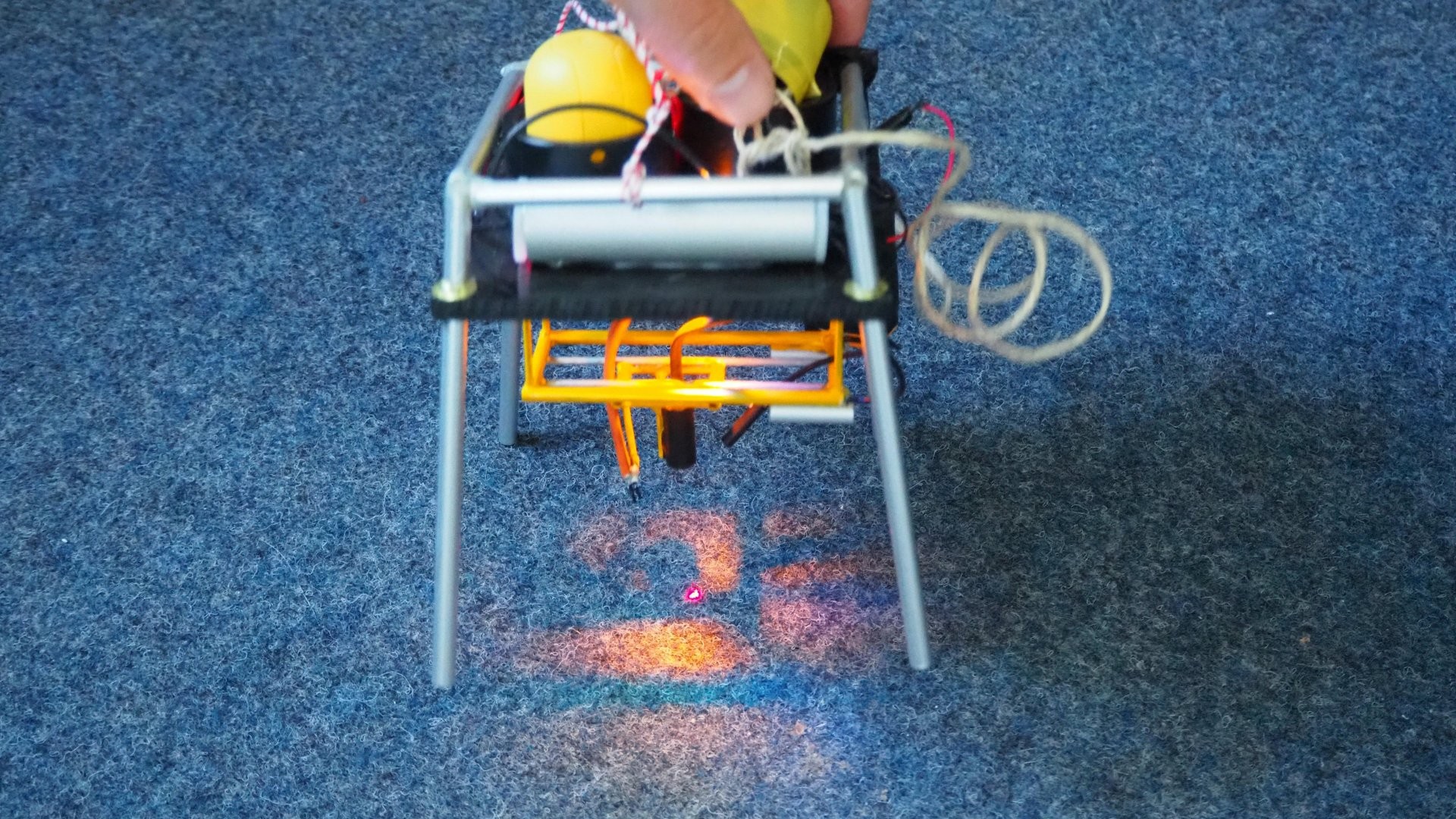
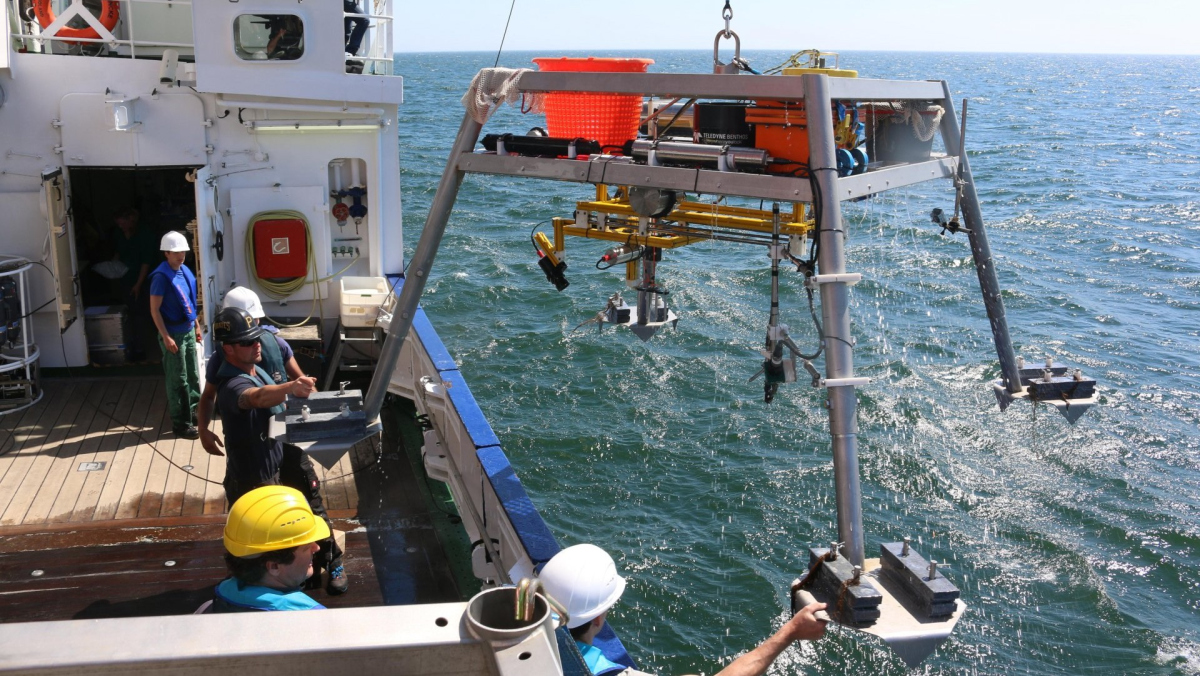
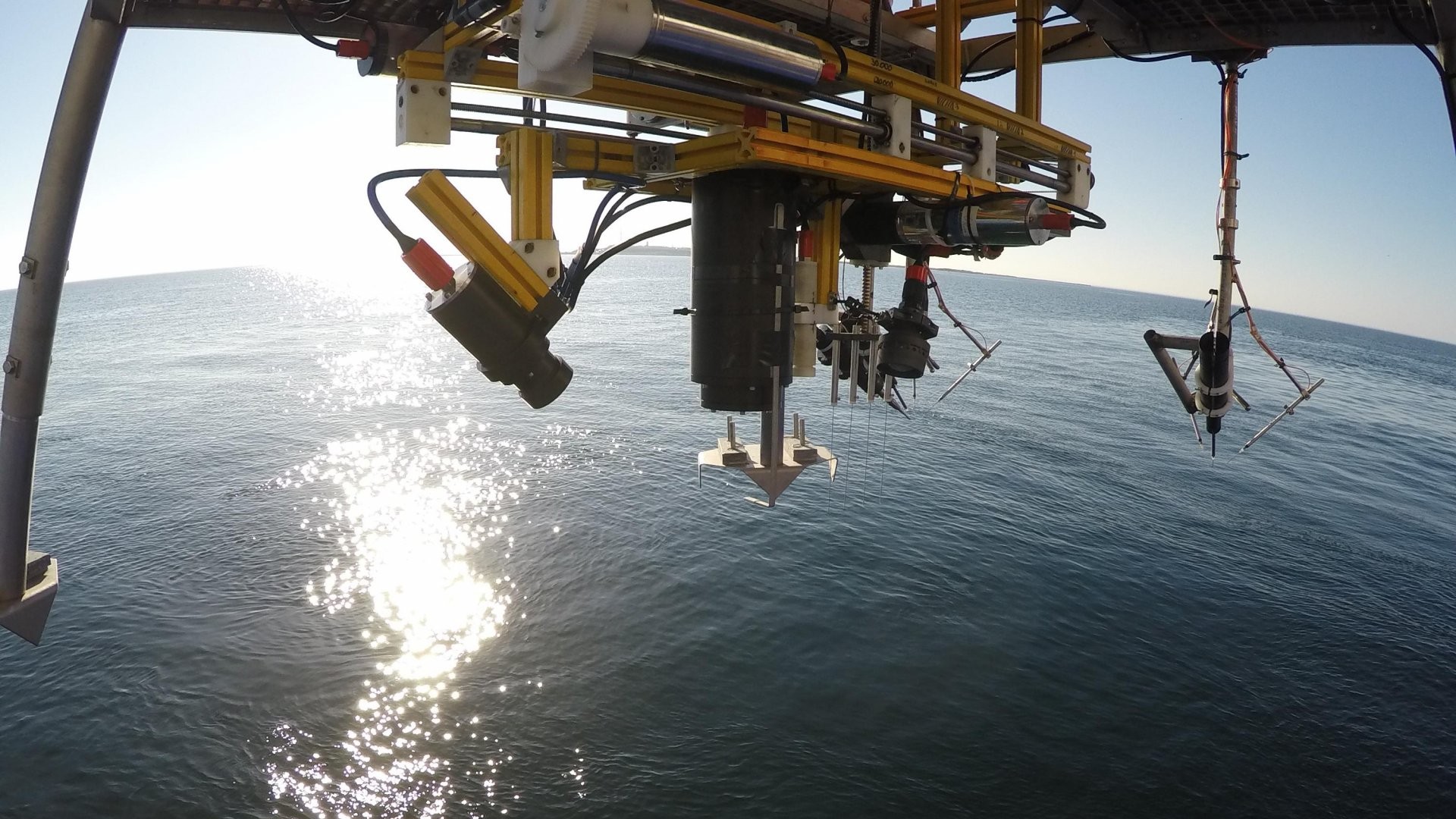
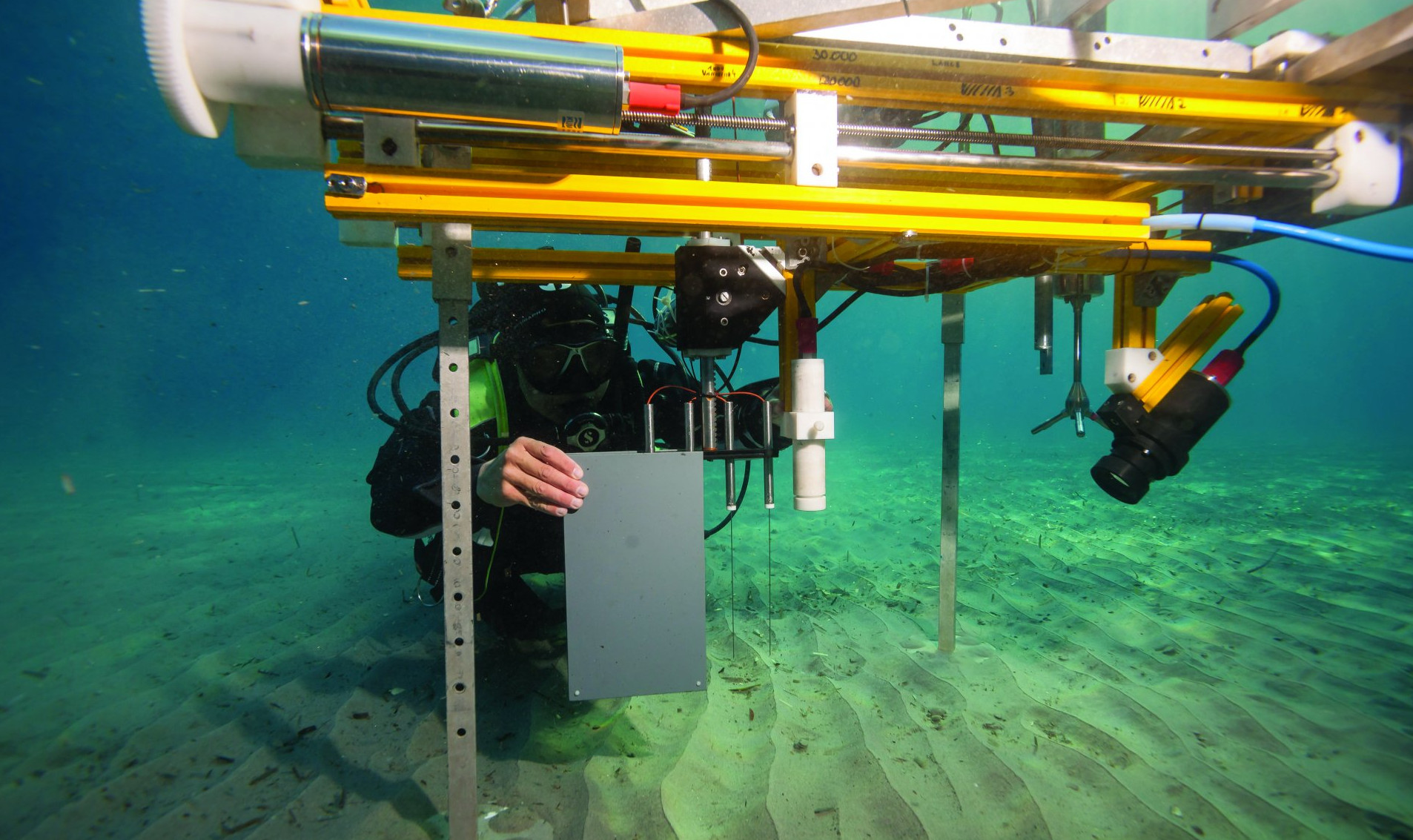
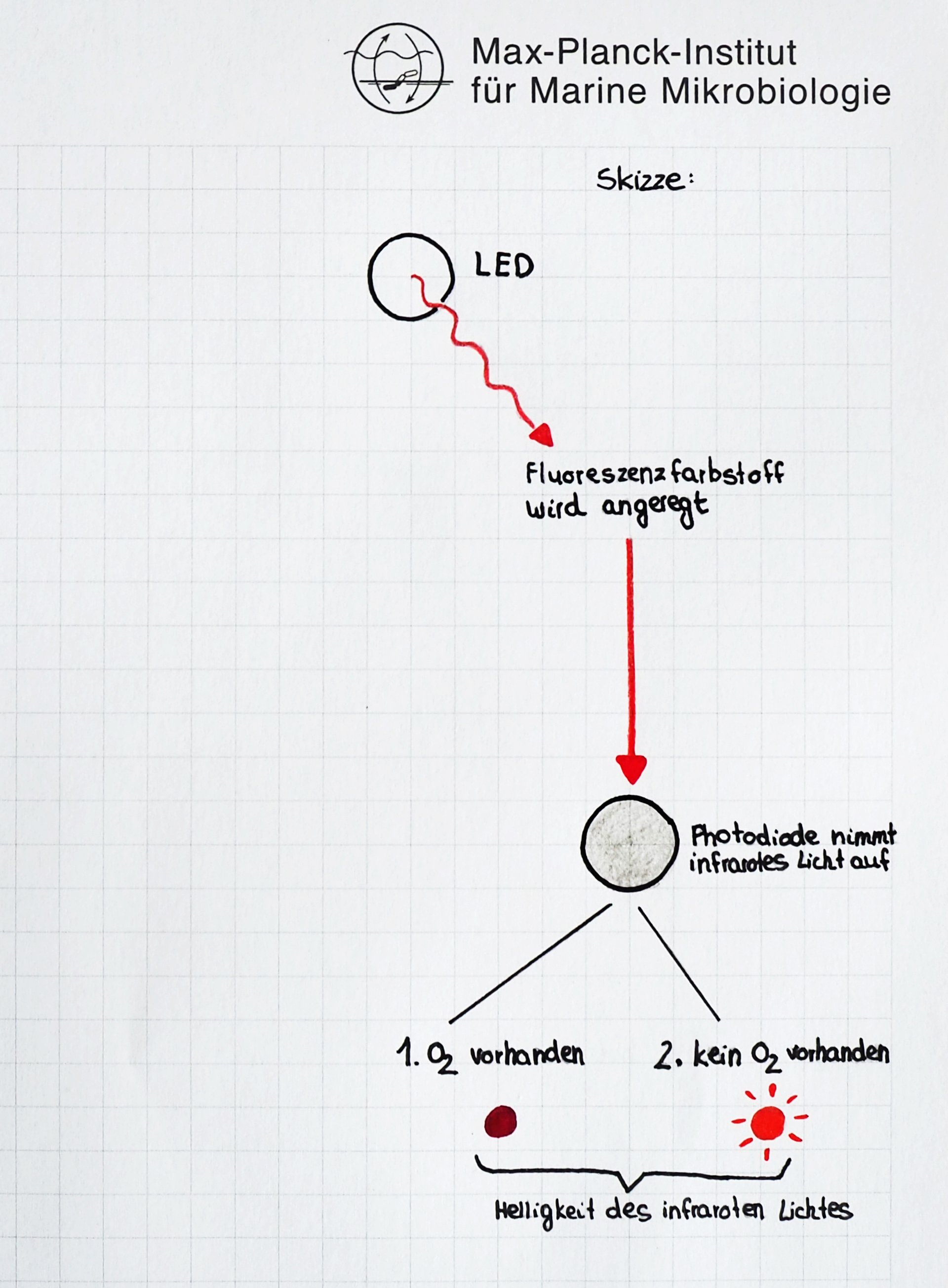
The Max-Planck-Institute for Marine Microbiology employs over 100 full time academic and about 50 non-academic staff. The Institute investigates the role, variety and characteristics of micro-organisms that occur in aquatic environments, i.e. the sea, and which are responsible in a decisive way for geochemical processes. A focus of the research rests in the marine sediments, which are sites of particularly intense and varied microbial processes. For the measurement of compounds at the surface and inside the sediment high spatial resolution analytical techniques are needed.