- Press Office
- Press releases 2020
- New ethane-munching microbes discovered at hot vents
New ethane-munching microbes discovered at hot vents
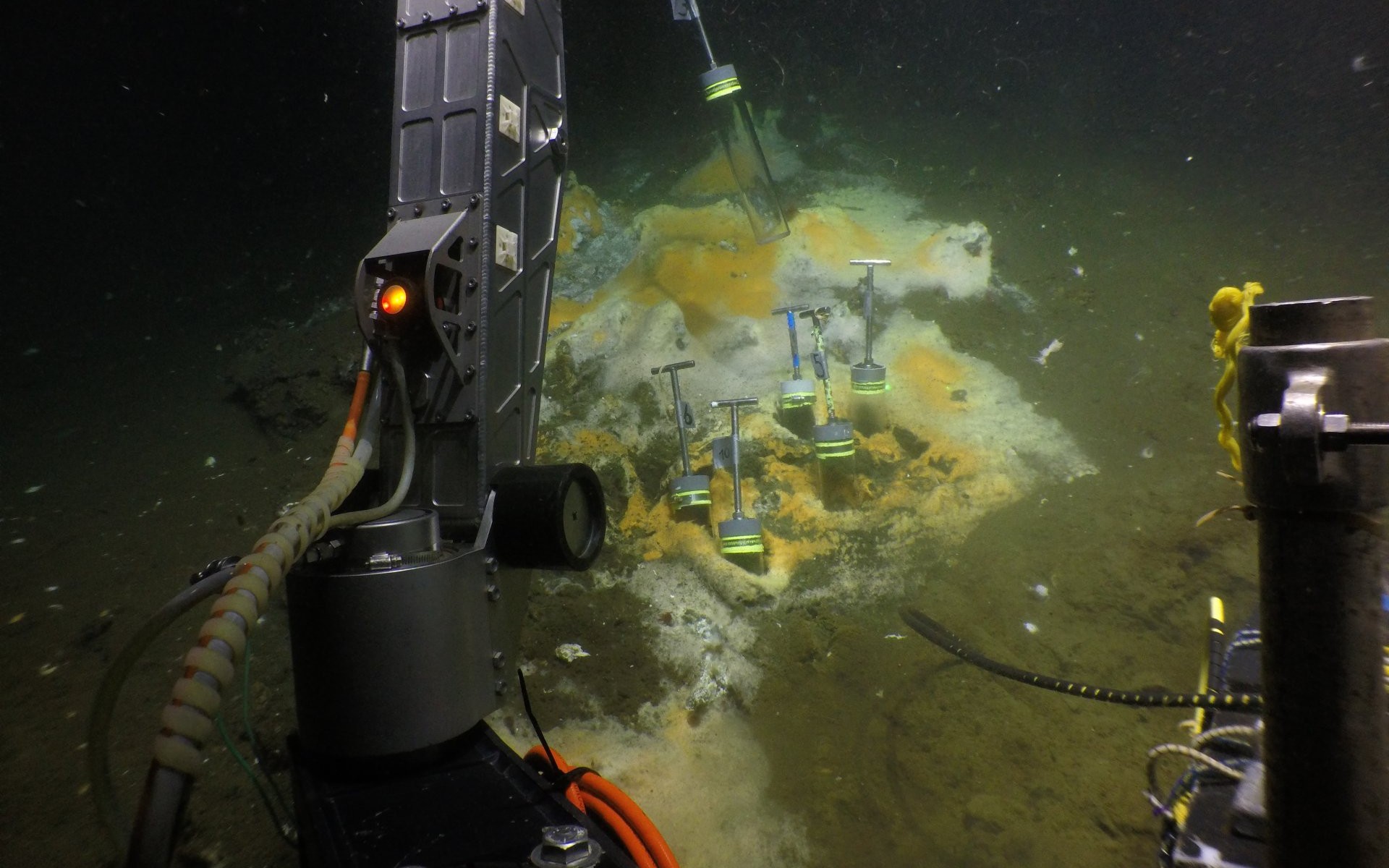

Unlike animals, which only digest proteins, carbohydrates and fats, microorganisms also feed on a variety of other organic compounds. Even natural gas does not stop them. Researchers from Bremen have now discovered a microbe in the deep sea that eats ethane, which, with a share of up to 15%, is the second most common component of natural gas.
Life in the extreme
The research group led by Gunter Wegener in cooperation with researchers from other institutes discovered the previously unknown microbe in the seafloor of the Guaymas Basin at a water depth of 2000 meters in the Gulf of California. “The Guaymas Basin is a natural laboratory teeming with new species,” Wegener said. “Responsible for this extraordinary diversity are hot fluids gushing out of the seafloor, which attract many different species. Already today, we have discovered many organisms in this habitat.”
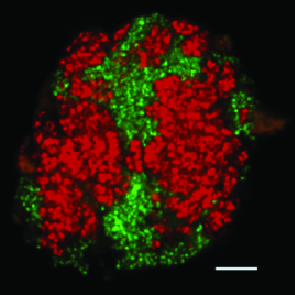
Degrading natural gas in teamwork
Some natural gas components such as propane or butane can be broken down by bacteria alone. However, in order to degrade the main components of natural gas – methane and ethane – two different organisms are necessary according to the present state of research, which form a so-called consortium: Archaea, which break down the natural gas, and bacteria, which couple the electrons released in the process to sulfate, an abundant compound in the ocean. Studying the biochemical processes in the consortia in the laboratory has been extremely challenging up to now: These organisms grow very slowly and only divide every few months. Thus, there was always little biomass available.
First time in laboratory culture
This is different with the ethane producers that have now been discovered: “These consortia are growing much faster,” reported Cedric Hahn, PhD student at the Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology and first author of the study. The cells double every week. “The laboratory cultures keep me pretty busy. But this way we now have enough biomass for extensive analyses. For example, we were able to identify key intercellular intermediates in ethane degradation. Also, we present the first complete genome of a natural gas-degrading archaea in this study.”
The newly discovered archaea was named Ethanoperedens thermophilum, which means “heat-loving ethane-eater”. Its partner bacteria are familiar from other consortia. Katrin Knittel, who has been working on the topic since the discovery of the first methane-munching consortia, said: “We have found gene sequences of these archaea at many deep-sea vents. Now we finally understand their function.”
Archaea could also convert carbon dioxide into ethane
The researchers also discovered something else: The ethane degradation of this microbe is reversible. Thus, relatives of Ethanoperedens could produce ethane from carbon dioxide. This is highly interesting for biotechnological applications. Wegener's team is now searching for such organisms. In addition, in cooperation with colleagues, they aim to convert microbes that produce methane into ethane producers. “We are not yet ready to understand all the steps involved in ethane degradation,” said Rafael Laso Pérez, who did his doctoral thesis on butane gas-degrading archaea. “We are currently investigating how Ethanoperedens can work so efficiently. If we understand its tricks, we could culture new archaea in the lab that could be used to obtain resources that currently have to be extracted from natural gas.”
This way, the microbes described here are significant for the global carbon cycle and the rising atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration in two ways: On the one hand, they use ethane in the deep sea and thus prevent this gas from reaching the atmosphere. On the other hand, they could offer a solution for the industry to reduce its carbon emissions. “This is still a long way off,” Wegener said. “But we are pursuing our research. One thing we know for sure: We shouldn't underestimate the smallest inhabitants of the sea!”
Original publication
Participating institutions
Max Planck Institute for Marine Microbiology, Bremen
MARUM, Center for Marine Environmental Sciences at the University of Bremen
Alfred Wegener Institute Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research, Bremerhaven
K.G Jebsen Centre for Deep Sea Research and Department of Biological Sciences
University of Patras, Patras, Greece
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Please direct your queries to
Scientist
HGF MPG Joint Research Group for Deep-Sea Ecology and Technology
MPI for Marine Microbiology
Celsiusstr. 1
D-28359 Bremen
Germany
|
Room: |
1335 |
|
Phone: |

Head of Press & Communications
MPI for Marine Microbiology
Celsiusstr. 1
D-28359 Bremen
Germany
|
Room: |
1345 |
|
Phone: |

